When we think about health, the spotlight usually falls on the heart, lungs, or brain. But the urinary and reproductive systems quietly influence our daily life and overall well-being. From something as common as kidney stones to more sensitive issues like male infertility or erectile dysfunction, problems in these systems can disrupt health, confidence, and relationships.
The good news? Modern urology and andrology offer advanced solutions, often minimally invasive, to help patients regain health and quality of life. This guide will help you understand the difference between the two specialties, major conditions they treat, treatment advances, and when to seek help.
What is Urology?
Urology is a medical specialty that deals with diseases of the urinary tract and male reproductive organs. Urologists treat:
- Kidneys (stones, infections, tumors).
- Bladder (infections, cancer, incontinence).
- Ureters and urethra (obstructions, strictures).
- Prostate (enlargement, cancer).
- Male reproductive system (in overlap with andrology).
A urologist may use medications, surgical techniques, or minimally invasive procedures to diagnose and manage conditions.
What is Andrology?
Andrology is a subspecialty of urology that focuses specifically on male reproductive and sexual health. While urology covers both men and women, andrology is the male equivalent of gynecology.
Andrologists specialize in:
- Male infertility.
- Erectile dysfunction (ED).
- Hormonal imbalances, especially testosterone.
- Men’s sexual health problems like premature ejaculation or Peyronie’s disease.
3. Major Areas of Urology (Expanded)
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are among the most widespread urological problems worldwide, affecting millions every year. They are hard mineral deposits that form when the urine becomes too concentrated with substances like calcium, oxalate, or uric acid.
Symptoms:
Patients often describe the pain of kidney stones as one of the worst they’ve ever felt. Classic symptoms include:
- Sudden, severe pain in the back or side that radiates to the groin.
- Blood in the urine, which may appear pink, red, or brown.
- Nausea, vomiting, and restlessness.
- Frequent urge to urinate, often with little output.
Treatment Options:
- RIRS (Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery): A minimally invasive procedure where a thin flexible scope is passed through the urinary tract to access and break stones inside the kidney. No external cuts are made, and recovery is usually quick.
- PCNL (Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy): Recommended for very large stones. A small incision is made in the back to directly access and remove the stone.
- URS (Ureteroscopy): Used for stones stuck in the ureter. A small scope is passed through the urinary tract to break and remove them.
- Shockwave Lithotripsy: Non-surgical method where sound waves are used to break the stone into small pieces that pass naturally through urine.
Key Takeaway: Timely treatment is crucial to prevent kidney damage and repeated infections.
Prostate Health
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder in men. With age, the prostate commonly enlarges — a condition called Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH).
Symptoms:
- Increased frequency of urination, especially at night (nocturia).
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination.
- Weak urine stream or dribbling.
- Feeling that the bladder isn’t fully emptied.
Treatment Options:
- Medications: Alpha-blockers to relax prostate muscles, or 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors to shrink the gland.
- Laser surgery: Minimally invasive, uses laser energy to remove excess prostate tissue.
- TURP (Transurethral Resection of the Prostate): The gold standard surgery, where part of the prostate is removed through the urethra to relieve obstruction.
Why It Matters: Ignoring prostate symptoms can lead to severe complications such as urinary retention, bladder stones, or even kidney damage.
Bladder Disorders
The bladder is central to urinary health, and disorders here can significantly affect quality of life.
Common Conditions:
- Overactive bladder: Strong, sudden urges to urinate, often leading to leakage.
- Urinary incontinence: Involuntary leakage of urine, which can be embarrassing and socially isolating.
- Bladder infections (UTIs): More common in women but equally troublesome in men, leading to burning urination and fever.
- Bladder cancer: Often presents with blood in the urine and requires early detection.
Treatment:
Management varies from simple lifestyle changes and medication to advanced surgeries depending on severity.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, most often E. coli.
Symptoms:
- Pain or burning while urinating.
- Cloudy, foul-smelling urine.
- Fever and pelvic discomfort.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics are the mainstay.
- Hydration helps flush out bacteria.
- Preventive measures include hygiene, urinating after intercourse, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use.
Why It’s Important: Untreated UTIs can progress to kidney infections, which are far more dangerous.
4. Major Areas of Andrology (Expanded)
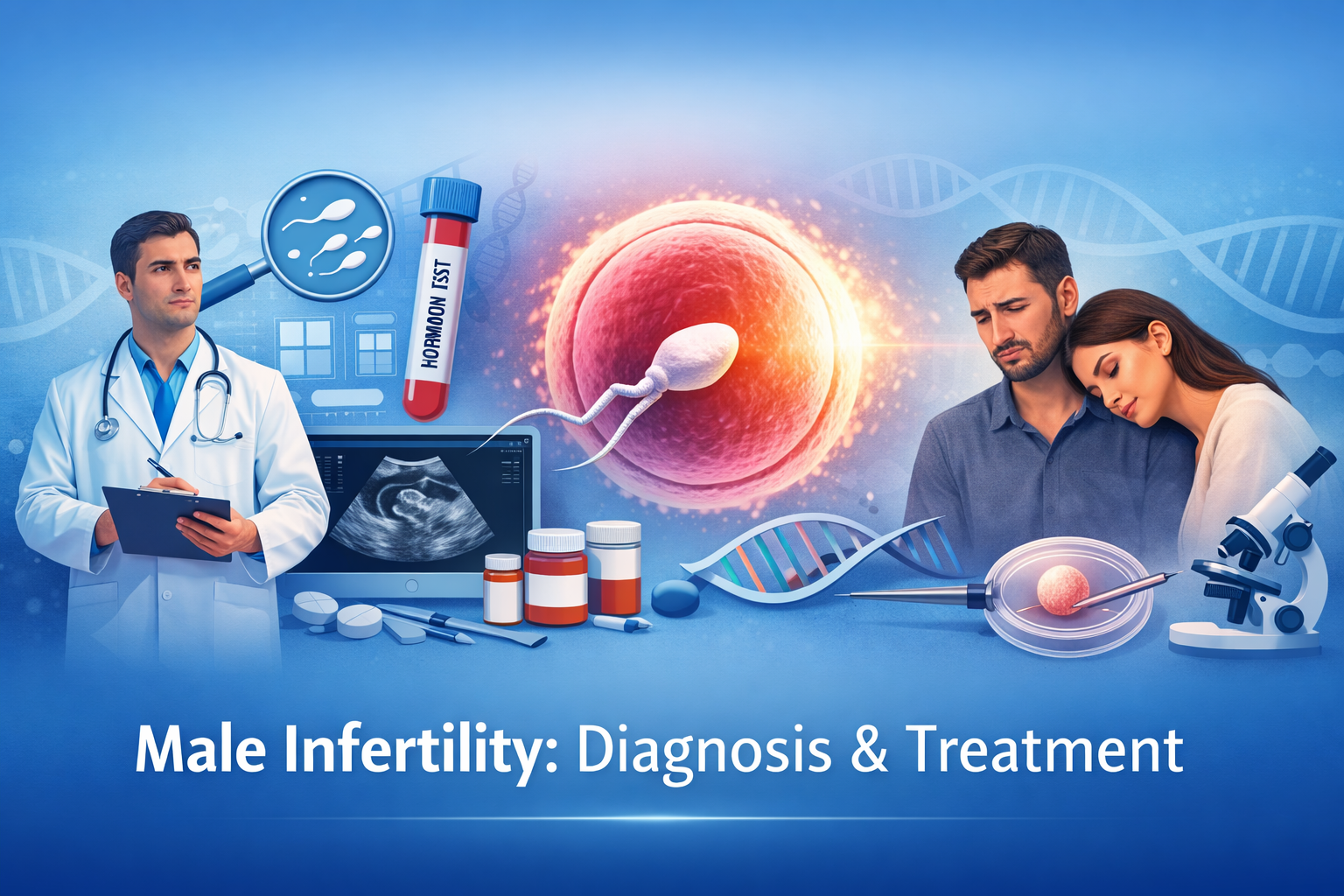
Male Infertility
Male infertility contributes to nearly 50% of infertility cases in couples. Causes include:
- Low sperm count or poor motility.
- Varicocele (enlarged veins around the testicle that affect sperm production).
- Genetic or hormonal problems.
- Lifestyle factors: smoking, alcohol, obesity, excessive heat exposure.
Treatments:
- Medication for hormonal or infection-related issues.
- Surgery to correct varicocele or remove blockages.
- Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART): IVF, ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection), sperm retrieval techniques like micro-TESE.
Note: Early diagnosis significantly improves success rates.
Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
ED is not just a sexual health issue — it can also be an early warning sign of cardiovascular disease.
Causes:
- Physical: diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, low testosterone.
- Psychological: stress, depression, performance anxiety.
- Lifestyle: smoking, alcohol, lack of exercise.
Treatment Options:
- Medications (PDE5 inhibitors like sildenafil).
- Testosterone replacement therapy if hormonal imbalance is detected.
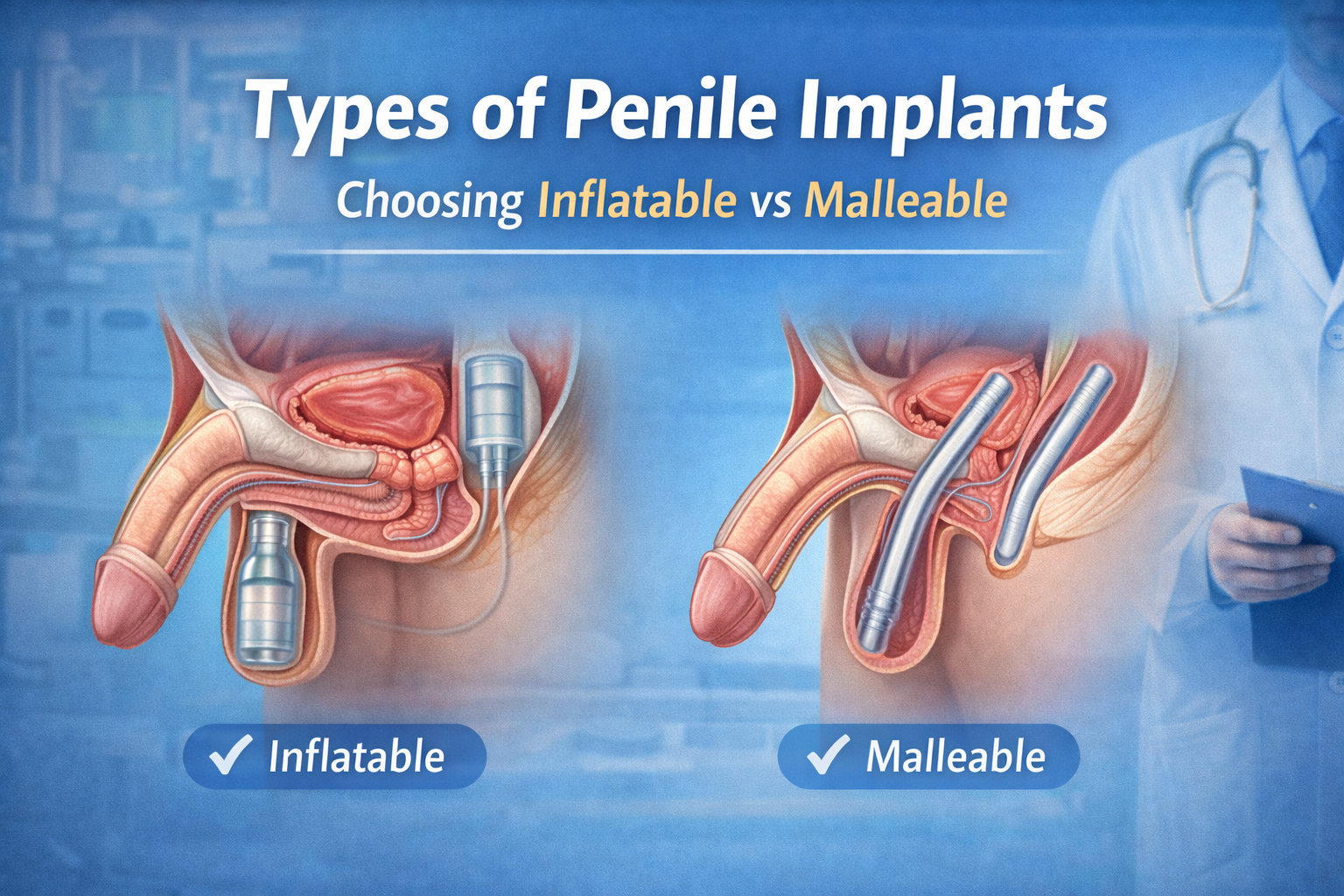
- Vacuum devices, injections, or penile implants for severe cases.
- Counseling/therapy if stress or psychological issues are involved.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones, especially testosterone, play a vital role in men’s health. Low testosterone can lead to:
- Chronic fatigue.
- Reduced libido.
- Loss of muscle mass and strength.
- Mood swings and irritability.
Management:
- Hormone replacement therapy under medical supervision.
- Lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, adequate sleep, and balanced diet.
- Addressing underlying health conditions such as diabetes or thyroid issues.
Men’s Sexual Health
Andrology also covers broader men’s sexual health concerns:
- Premature ejaculation – very common but treatable through medication and behavioral therapy.
- Peyronie’s disease – abnormal curvature of the penis due to scar tissue.
- General performance concerns – requiring a mix of medical and psychological support.
Why It Matters: These issues affect confidence, relationships, and mental well-being. Seeking timely care is essential.
5. Advances in Urology & Andrology Treatments (Expanded)
The last decade has seen revolutionary progress in treatments:
- Laser surgeries for kidney stones and prostate, ensuring quicker recovery.
- Robotic-assisted surgeries offering unmatched precision with smaller incisions.
- Micro-TESE (microsurgical sperm retrieval) for men with severe infertility.
- Sperm banking & fertility preservation for men undergoing cancer treatments.
- Advanced imaging (MRI, 3D ultrasound) for early detection of prostate, kidney, and testicular issues.
6. When Should You See a Specialist? (Expanded)
See a Urologist if:
- You have severe or recurring back/side pain that may indicate stones.
- Blood in urine (always a red flag).
- Painful or difficult urination.
- Frequent UTIs or bladder control issues.
- Prostate symptoms like weak urine flow, frequent night urination.
See an Andrologist if:
- You and your partner have been trying to conceive for over a year without success.
- You experience erectile dysfunction more than occasionally.
- You have low libido, fatigue, or other hormonal imbalance symptoms.
- You face performance issues or abnormalities in sexual function.
7. Prevention & Lifestyle Tips (Expanded)
- Hydration: Drink at least 2–3 liters of water daily to keep kidneys healthy and prevent stones.
- Balanced diet: Reduce salt, processed foods, and red meat; increase fruits and vegetables.
- Exercise: Helps maintain hormonal balance, fertility, and overall urological health.
- Avoid smoking & alcohol: Both are linked to ED, infertility, and bladder cancer.
- Maintain healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for both urological and andrological problems.
- Annual checkups: Especially after age 40, to catch issues early.
8. Choosing the Best Urologist or Andrologist (Expanded)
Finding the right specialist can feel overwhelming. Consider:
- Qualifications & certifications – Are they trained in advanced procedures?
- Experience in your condition – e.g., kidney stone expert vs. male infertility specialist.
- Technology available – Do they offer minimally invasive or robotic options?
- Patient testimonials – Word-of-mouth and online reviews.
- Approach to care – Do they explain clearly, show empathy, and provide comprehensive treatment (not just a quick fix)?
Conclusion
Urological and andrological health is not something to ignore. From kidney stones to male fertility issues, the earlier you seek care, the better the outcome. With modern, minimally invasive treatments and specialists like Dr. Ashish Saini, patients today have access to world-class solutions that restore health, confidence, and quality of life.