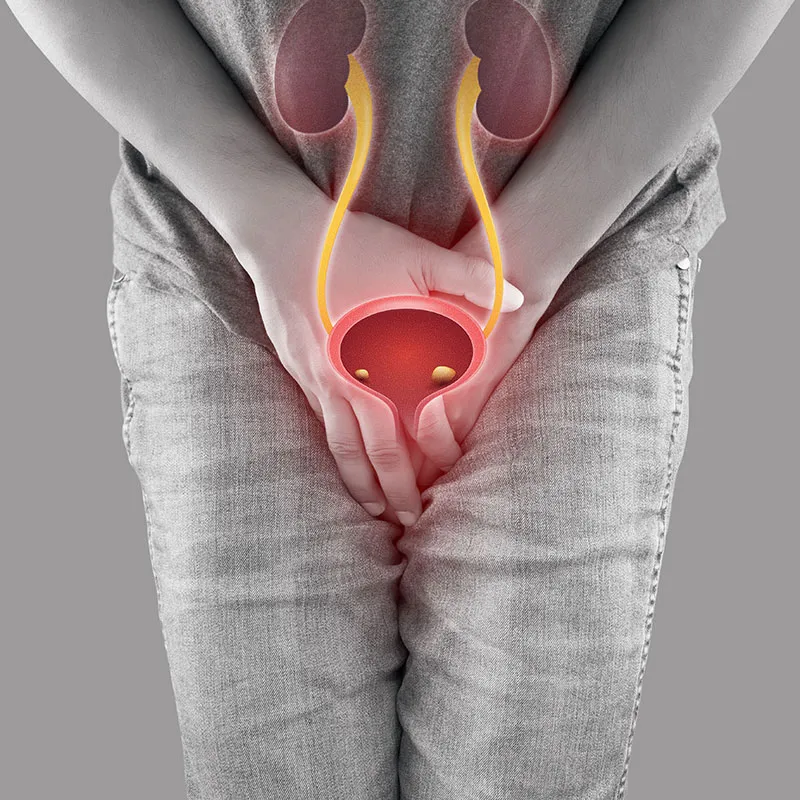
Urethra: A Vital Pathway in Men and Women
The urethra is a crucial part of the urinary system, transporting urine from the bladder to the body’s exterior. In men, the urethra also plays a role in the reproductive system by serving as the conduit for semen during ejaculation. Given its importance, any disruption or condition affecting the urethra can have significant implications. This article explores various urethral conditions, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention measures.What is Urethral Stricture?
Imagine your urethra as a tiny tube carrying urine from your bladder out of your body. Now, picture a situation where this tube becomes narrow or even blocked. That’s what we call a Urethral structure.Causes:
- Scar tissue formation due to inflammation or injury
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Surgical procedures involving the urethra
Symptoms:
- Difficulty initiating or maintaining a urine stream
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Pain or burning during urination
- Discharge from the urethra

Treatment:
- Urethral dilation
- Urethrotomy (surgical incision)
- Urethroplasty (reconstructive surgery)
Prevention:
To prevent urethral strictures, practicing safe sex to avoid sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and getting prompt treatment for urinary tract infections can be helpful. A urethral stricture is like a traffic jam in your urinary highway, making it more challenging for urine to flow smoothly. If you notice any signs or symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for the correct diagnosis and treatment.Urethral Trauma
What is Urethral trauma?
Urethral trauma refers to any injury or damage to the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. This type of injury can occur in both men and women and may result from various causes, ranging from accidents and injuries to medical procedures.Causes:
- Accidents or injuries to the pelvic region
- Catheterization procedures
- Penetrating injuries
Symptoms:
The symptoms of urethral trauma can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but common signs include:- Presence of blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Pain or tenderness in the genital area
- Difficulty or pain during urination
- Swelling or bruising around the pelvic region

Treatment:
- Observation for mild cases
- Surgical repair for severe trauma
- Catheterization for temporary relief
Prevention:
Preventing urethral trauma involves taking precautions with potential risks, such as using protective gear during sports and ensuring the proper and gentle insertion of catheters in medical procedures. It’s essential for individuals who suspect urethral trauma or experience related symptoms to seek prompt medical attention. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for a successful recovery and to prevent potential complications.What is Urethritis (Chlamydia/Gonorrhea)
Urethritis is the inflammation of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body.Causes:
- Bacterial infections, commonly Chlamydia or Gonorrhea
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
Symptoms:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Discharge from the urethra
- Frequent urination
Treatment:
- Antibiotics specific to the causative bacteria
- Partner treatment to prevent re-infection

Prevention:
- Safe Sex Practices: Using condoms or dental dams during sexual activity can reduce the risk of bacterial or viral infections.
- Avoiding Irritants: Minimizing exposure to potential irritants, such as harsh soaps or chemicals.
Meatal stenosis is a condition characterized by the narrowing or
constriction of the opening of the urethra, known as the meatus. This
narrowing can obstruct the flow of urine from the body and lead to
various urinary symptoms. While meatal stenosis is more commonly
observed in males, it can also affect females.
Causes:
- Previous circumcision, particularly in males
- Trauma or injury to the meatus
- Infection or inflammation of the urethra
- Congenital abnormalities

Symptoms:
The symptoms of meatal stenosis may include:- Difficulty or pain during urination
- Narrowing or spraying of the urinary stream
- Dribbling of urine after urination
- Urinary tract infections
- Redness or irritation around the meatus
Treatment:
Treatment options for meatal stenosis depend on the severity of the condition and may include:- Observation and monitoring for mild cases
- Topical medications to reduce inflammation
- Dilation of the meatus using special instruments
- Surgical correction to widen the opening (meatoplasty)
Prevention:
Preventing meatal stenosis involves minimizing the risk factors associated with its development, such as:- Avoiding unnecessary trauma to the genital area
- Practicing good hygiene to prevent infections
- Seeking prompt medical attention for urinary symptoms
Urethral Discharge
What is Urethral Discharge
Urethral discharge refers to the abnormal release of fluid from the urethra, the tube responsible for transporting urine from the bladder out of the body.Causes:
- Infection, including STIs
- Inflammation
- Trauma
Symptoms:
- Abnormal discharge from the urethra
- Itching or burning sensation
- Redness and swelling
Treatment:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Antifungal medications for fungal infections
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
Prevention:
- Safe sex practices
- Prompt treatment of infections
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
What is Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs), also known as Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs), are a group of infections that are primarily transmitted through sexual contact. These infections can affect various body parts, including the genitals, mouth, and rectum.Causes:
- Various bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
Symptoms:
- Vary based on the specific STD but may include urethral discharge, pain, and itching
Treatment:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Antiviral medications for viral infections

Prevention:
- Safe sex practices
- Vaccination for preventable STDs