
Early detection and treatment of cancer are fundamental to its management. Despite the fact that screening programs increase the likelihood of discovery, it is yet unknown if early diagnosis and treatment of small-bulk localized prostate cancer causes would result in a general decline in death. Radical prostatectomy, radiation, and surveillance are the available management choices, however, there is little information to assess the merits of each strategy. Hormone treatment for prostate cancer is used to manage the advanced level of the same. With the adoption of more compassionate methods of treatment and advancements in both chemotherapy and radiation, there have been significant advances in treatment over the past 20 years.
This article by one of the top urologists in Delhi, Dr Ashish Saini aims to broaden one’s knowledge of what is prostate cancer and how it can be treated. Also, get to know under what circumstances you should have prostate laser surgery.
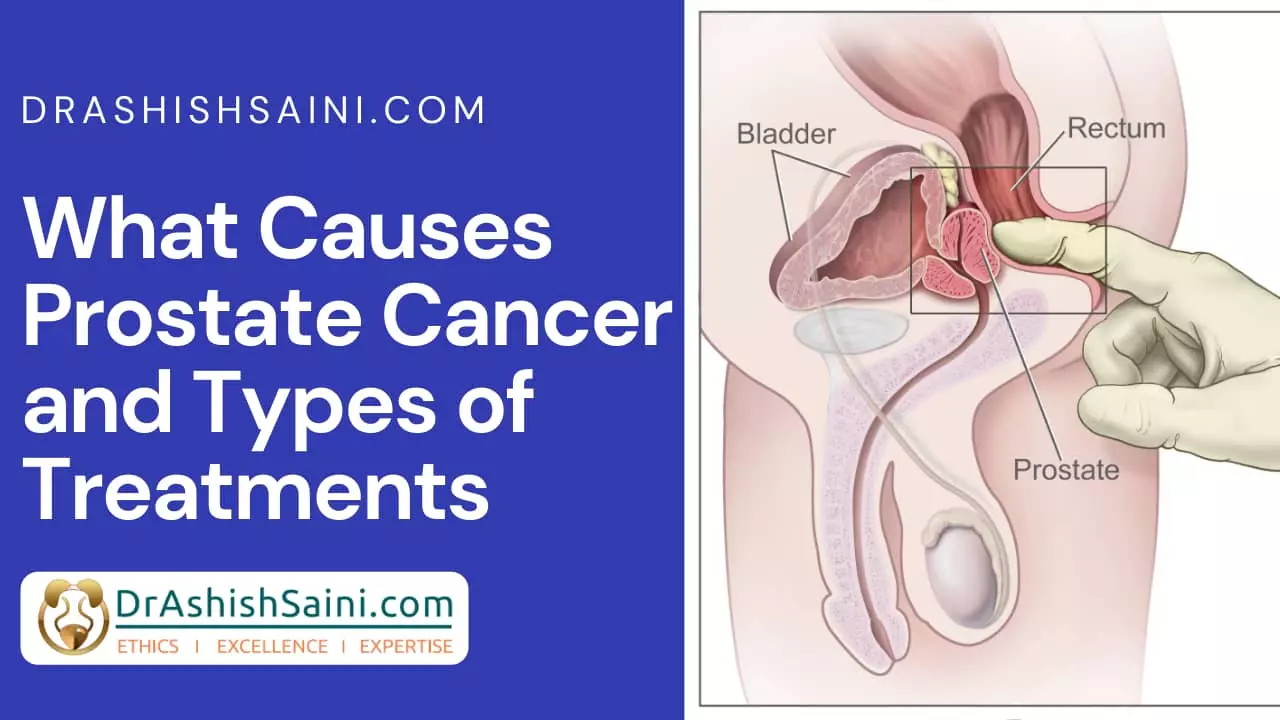
What is a Prostate?
The prostate is a little gland that aids in the storage of seminal secretions and is situated close to the base of the penis. Semen is made up of these fluids, and the prostate also aids in pushing semen through the urethra. In order to promote the ideal flow of sperm and seminal fluids, the prostate is a crucial organ. However, because of its proximity, urinary infections frequently also affect the prostate gland.
In other words, the prostate and seminal vesicles’ primary function is to produce fluid to bathe semen. Sperm is produced in the testicles during ejaculation and then travels to the urethra. The seminal vesicles and the prostate’s fluid both enter the urethra at the same moment. The ejaculate, which exits the penis through the urethra, is made up of a mixture of semen, fluid from the prostate, and seminal vesicles.
What is Prostate Cancer?
Cancer that develops in the prostate is known as prostate cancer. In males, the prostate is a little walnut-shaped gland that secretes seminal fluid, which feeds and carries sperm.
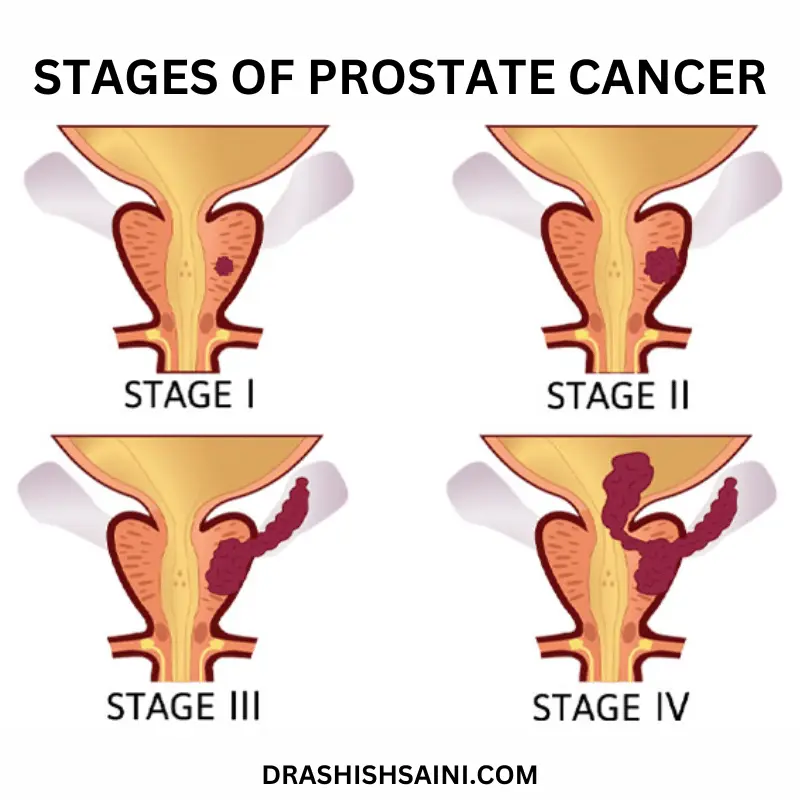
One of the most prevalent cancers is prostate cancer. In the prostate gland, where they may not do much harm, many prostate tumours develop slowly and are localized. Although some cancers spread slowly and may require little to no therapy, others are aggressive and can spread very quickly. Early-stage prostate cancer that is still contained to the prostate gland provides the best prognosis for recovery. It is best to however try and avoid landing with prostate cancer reasons so as to be very safe in the future with all the complications.
What are the common Prostate Diseases?
- An infection of the urinary tract may or may not be the cause of prostate cancer, prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate gland. A burning feeling while passing urine, discomfort in the lower abdomen, pain before or after ejaculation, and a moderate temperature are all signs of prostatitis.
- Enlarged prostate symptoms: BPH, often known as an enlarged prostate, is a condition in which the prostate gland grows larger than usual. This causes issues urinating and results in persistent lower-abdominal heaviness.
- Prostate cancer reasons: The enlarged prostate symptoms occasionally begin to form tumour-like growths, which are typically malignant. When the prostate is removed, this cancer can be completely cured if detected in its early stages.
Prostate Cancer Symptoms include-:
Prostate cancer symptoms cannot be detected early, but screening might find alterations that can be cancerous. Using a test, screening can determine how much PSA is present in the blood. High levels imply the possibility of malignancy.
Men who do have prostate cancer symptoms might notice
- Inability to begin and maintain urinating
- A persistent urge to urinate, particularly at night, a weak urine stream, and blood or semen in the urine
- Back, hips, or pelvic pain during urination or ejaculation
It is also important to note that Prostate cancer symptoms vary from person to person. Some males experience no enlarged prostate symptoms at all.
Top Reasons for Prostate Cancer or Causes of Prostate Cancer
The exact causes of prostate cancer are unknown. Prostate cells change their DNA, which is how doctors know prostate cancer starts.
- Family History: In some cases, the mutation is one of the causes of prostate cancer that is inherited and is passed on to family members especially if your father or brother is dealing with prostate then there are more chances of you getting a prostate.
- Age: Age is the second most common factor for causes of prostate cancer. Reasons for prostate cancer in young males especially those under the age of 40 have less chance of the same, but men over the age of 65 have increased risks of developing the disease, according to studies. This adds to another one of the reasons for prostate cancer
- Diet: It is found that people who follow a diet that is rich in dairy products, red meat, or foods that are high in fats are most often at risk of developing enlarged prostate after a certain age as mentioned above point.
- Enlarged Prostate: An uncured enlarged prostate symptoms can convert into a cause of prostate cancer if they are not treated for a longer period of time. Hence, to avoid prostate cancer and to avoid adding to another reason for prostate cancer, the enlarged prostate needs to be treated as soon as you find any symptoms.
- Race. Reasons for prostate cancer that are not yet determined, Black people have a greater risk of prostate cancer than do people of other races. In Black people, this type of cancer is also more likely to be aggressive or advanced.
- Obesity. People who are obese may have a higher risk of prostate cancer compared with people considered to have a healthy weight, though studies have had mixed results. In obese people, the cancer is more likely to be more aggressive and more likely to return after initial treatment for prostate cancer aiding further reasons for prostate cancer.
Treatment for Prostate Cancer
- Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A laparoscope is inserted inside the abdomen with the help of a few small incisions. This minimally invasive surgery then takes out the prostate gland with the help of the laparoscopic tools along with its vessels. This treatment for prostate cancer is considered one of the best it does not spread to other organs or in the bloodstream.
- Open Radical Prostatectomy: This open surgery involves the removal of the prostate gland and its related vesicles by making an incision (8 to 10 cm) near the umbilical area.
- External radiation therapy: This treatment for prostate cancer sends radiation to the cancer cells from a machine outside the body. A type of external radiation known as conformal radiation therapy employs a computer to help guide and target a particular spot, reducing the risk to healthy tissue and enabling a high dose of radiation to reach the prostate tumour.
- Internal radiation therapy, also known as brachytherapy, is a treatment for prostate cancer that involves the implantation of radioactive seeds close to the prostate by a physician. A surgeon utilizes imaging tests like computed tomography or ultrasound to assist direct where to place the radioactive material.
- Chemotherapy: This treatment for prostate cancer approach makes use of medications to slow the spread of cancer cells. Although it can eradicate cancer cells all over the body, there could be negative effects.
- Hormonal therapy: Androgens are male hormones used in hormonal therapy. Testosterone and dihydrotestosterone are the two primary androgens. The proliferation of cancer cells appears to be stopped or delayed by blocking or decreasing these hormones. One choice is to have the testicles, which are responsible for producing most of the body’s hormones, surgically removed. Other medications may be helpful.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment for prostate cancer makes use of the immune system to combat cancer. To assist strengthen or restore the body’s natural defences against cancer, scientists can employ compounds the body makes or make them in a lab.
- Targeted therapy: This technique employs medications or other chemicals that recognize and kill particular cancer cells. For instance, a study from 2021 spotlights a radiopharmaceutical treatment for prostate cancer strategy that could be successful for difficult-to-treat kinds of advanced prostate cancer.
- Laser Therapy: The extreme heat produced by prostate laser surgery is focused light. Prostate laser surgery comes in a variety of forms, including:
- Prostate photo-selective vaporization (PVP). To remove extra prostate tissue and widen the urinary channel, a laser is employed. Treatment for prostates that are mild to moderately enlarged typically involves this operation.
- Prostate holmium laser ablation (HoLAP). Similar to PVP, but using a different kind of laser, is this technique.
Your doctor’s recommendation for prostate laser surgery will rely on a number of variables, including Your well-being, the kind of laser technology that is accessible, your physician’s education, and the size of your prostate also if you have any prostate cancer symptoms.
You can reduce your risk of prostate cancer if you:
- Pick a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables. A variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains should be consumed. Numerous vitamins and elements found in fruits and vegetables can benefit your health.
- Discuss the increased risk of prostate cancer with your doctor. If your risk of developing prostate cancer is very high, you and your doctor may discuss taking drugs or undergoing other treatments to lower that risk. According to certain research, using 5-alpha reductase inhibitors like dutasteride (Avodart) and finasteride (Propecia, Proscar) may lower the overall chance of getting prostate cancer. These medications are used to manage hair loss and enlargement of the prostate gland.
[elementor-template id=”1978″]
Bringing it all together about Treatment for Prostate Cancer
Although enlarged prostate is a prevalent condition, doctors can identify the majority of cases early and offer efficient therapy. Men with localized or regional prostate cancer have a nearly 100% 5-year survival rate, while men with distant cancer have a 30% survival rate. Currently, 98% of people survive for five years overall.
Treatment for prostate cancer can include medication, minimally invasive procedures, and surgery. It’s important to work with a urologist, who specializes in treating conditions of the urinary tract and male reproductive system, to determine the best course of treatment for you.Regular screening is the greatest approach to finding and avoiding prostate cancer reasons in its earliest stages. Depending on risk factors, screening may be best started at age 40. Anyone who has not yet undergone screening should discuss their choices with Dr Ashish Saini at Excel Advanced Urology Center in order to figure out prostate cancer reasons if there are any.
This was all about Prostate cancer. Myths about any problem can lead to misconceptions about it. Don’t miss out on our article about Myths About Prostate Cancer.
FAQ’s
1. What is the latest treatment for enlarged prostate?
The symptoms worsen as males age. Medication and treatments that burn the prostate from the inside out, including prostate laser surgery or electric loops, have long been used to treat BPH. However, a recently developed convective water therapy procedure employs steam to shrink the prostate.
2. How quickly does prostate cancer spread?
Prostate cancer can metastasize (spread to other areas of the body) over a period of up to 15 years, usually to the bones. It frequently has little impact on a man’s natural life expectancy.
3. What are the signs that prostate cancer is getting worse?
The most typical signs and symptoms include pain and edoema at the site of cancer’s spread. Cancerous cells can obstruct lymph fluid’s ability to drain. As a result of fluid accumulation there, this may cause swelling in the legs. We refer to the swelling as lymphoedema.
4. What is the most common problem after prostatectomy?
Urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction are the two main potential adverse effects of radical prostatectomy (impotence; problems getting or keeping erections). Other prostate cancer treatments may potentially cause the same side effects.
5. How long do you have incontinence after prostate surgery?
In the weeks following the removal of the catheter, most patients regain control. Within 3 to 18 months following surgery, the vast majority of men who had normal urine control before to the treatment regain it.
6. Is prostate removal surgery dangerous?
Serious consequences are uncommon, despite the surgery being the most invasive for treating an enlarged prostate. The majority of men who undergo the operation often don’t require any BPH follow-up care.